The year 2019 at the IHTE UB RAS began with the annual training of employees dedicated to the first aid techniques in case of accidents. The head of the laboratory of medical materials and bioceramics, PhD (medical sciences), Mikhail V. Gilev, delivered a lecture and demonstrated techniques for the first-aid. We put a short reminder how not to get confused in case of an emergency, but try to provide the first aid and probably save someone’s life.
 1. Take care of yourself. Make sure that nothing threatens you, because otherwise you will not be able to provide help.
1. Take care of yourself. Make sure that nothing threatens you, because otherwise you will not be able to provide help.
2. Protect the victim. Examine it, check for signs of life (pulse, respiration, reaction of pupils to light) and consciousness.
3. Call an ambulance: 112 – from a mobile phone, from a city phone – 03 (ambulance) or 01 (rescuers).
4. Provide emergency first aid. Provide comfort to the affected person and wait for the arrival of specialists.
4.1 Artificial respiration. If during the examination of the victim natural breathing is not detected, it is necessary to immediately carry out this procedure.
- Check the airways and, if necessary, clean them from mucus, blood, foreign objects (preferably with cotton buds (disks), if not, then gently with your hands).
- Tilt the victim’s head back; hold the neck with one hand
-
Put a tissue, handkerchief, piece of cloth, or gauze on the victim’s mouth. So you protect yourself from infection (it is important to remember about your safety).
-
Pinch the victim’s nose with your thumb and forefinger. Take a deep breath; press your lips tightly against the victim’s mouth. Exhale into the victim’s lungs. The first 5–10 breaths should be fast (in 20–30 seconds), then – 12–15 breaths per minute.
- Then just watch the victim’s lungs and wait for the breathing to return.
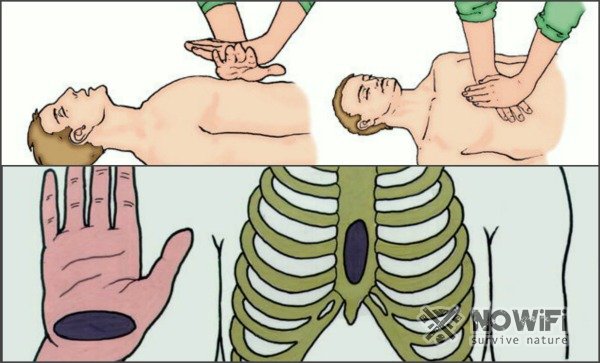
 4.2 Indirect heart massage. If, along with breathing, there is no pulse, it is necessary to perform an indirect heart massage:To do this, lay the victim on a flat hard surface. You cannot carry out this procedure on the bed and other soft planes.
4.2 Indirect heart massage. If, along with breathing, there is no pulse, it is necessary to perform an indirect heart massage:To do this, lay the victim on a flat hard surface. You cannot carry out this procedure on the bed and other soft planes.
- The most important thing is to determine the location of the xiphoid appendix. The xiphoid appendix is the most short and narrow part of the sternum, its end. Find the connecting rib bone. Its end is the xiphoid appendix.
- Measure 2–4 cm up from the xiphoid appendix – this is the point, at which you need to work with a massage.
- Place the base of the palm on the point of the xiphoid appendix. The thumb should point to either the chin or the abdomen of the victim, depending on the location of the person performing the resuscitation. On top of one hand, you must put a second hand, fingers folded into the lock. Pressing should be done strictly with the base of the palm – the fingers should not touch the victim’s sternum.
-
Perform rhythmic thrusts of the chest strongly, smoothly, vertically, with the weight of the upper half of your body. The frequency is 100–110 pressings per minute. In this case, the chest should bend at 3-4 cm.
-
If each item is correctly performed, the victim will breathe and pulse will appear. After that, you need to lay a man on his side and put his hand under his head.
4.3 Stemming of a glow of blood. The first task in the treatment of any significantly bleeding wounds is to stop the bleeding. It is necessary to act at the same time quickly and purposefully, since a significant loss of blood during an injury weakens the victim and poses a threat to his life.
A tourniquet (not always) stops only arterial blood: it beats with a strong pulsating jet. Venous blood runs out continuously, and capillary blood flows evenly from the wound, like from a sponge.
Before applying the tourniquet, press the artery with your fingers above the wound as soon as possible, in the place where it comes closest to the surface of the body. So the blood will be stopped almost instantly, and after that it will be possible to make a constriction, but only until the bleeding stops, not tighter. It is important to remember:
- The tourniquet does not impose on bare skin: only on top of clothes, a piece of cloth or bandage
- The tourniquet cannot be covered with anything – it must be visible
- The tourniquet can be left no more than 2 hours in the summer and 1.5 hours in the winter (outside), for children this time is reduced by half
- You need to record the time of application of the tourniquet for medical workers; put a piece of paper under the tourniquet.
-
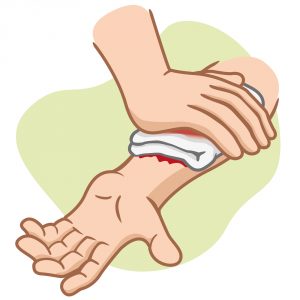
For other bleedings, even heavy ones, a tight dressing is enough: pin a dense roller of sterile wipes to the wound and apply new dressings over the old ones as it is soaked. So the doctors will understand the level of blood loss.
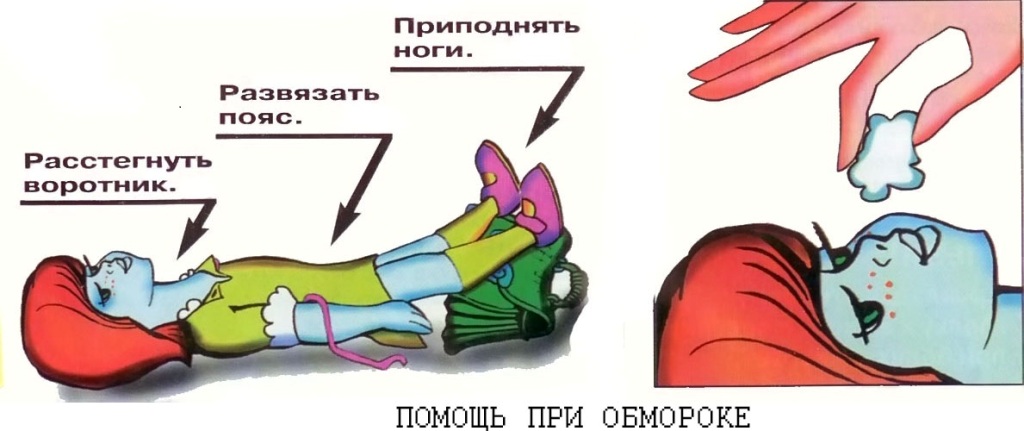
4.4 Help with fainting. Fainting is a sudden loss of consciousness due to a temporary impairment of cerebral blood flow. In other words, it is a signal from the brain that it lacks oxygen. To identify a person close to fainting is simple. His eyes begin to roll, his body becomes covered with cold sweat, his pulse weakens, and his extremities grow cold.
- If a person fainted, give him a comfortable horizontal position and provide fresh air (undo the clothes, loosen the belt, open windows and doors).
- Splash cold water on the victim’s face and pat him on the cheeks.
- If you have a first-aid kit on hand, let a person smell a cotton swab dipped in liquid ammonia.
If consciousness does not return for 3-5 minutes, immediately call an ambulance.